Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is the space research organization of India. Currently, it ranks 6th among the largest space agencies in the world.
In this post, we are trying to cover everything there is to know about ISRO, including all the exam-relevant points.
For Kerala PSC, UPSC, and all other important competitive examinations, there are generally one or two GK questions about ISRO in the Science & Technology / Current Affairs section.
Basic Facts
- Established - 1969 August 15.
- Headquarters – Antariksh Bhavan, Bangalore.
- Vision – Harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration.
- Under Department of Space (DOS, June 1, 1972).
- Until 1972, under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
- Department of Atomic Energy was established in -1954.
- First Chairman – Homi J. Bhabha.
- Father of ISRO – Dr. Vikram Sarabhai.
- First Chairman – Dr. Vikram Sarabhai.
- First Malayali Chairman – M.G.K. Menon.
- Longest Served Chairman – Dr. Satish Dhawan.
- Current ISRO Chairman – S. Somanath.
- Department of Space (DOS) & the Space Commission – 1972
- Indian astronauts are commonly known as – Vyomnauts.
- Missile Testing Center of India - Wheeler Island (Odisha).
- Renamed as Abdul Kalam Island (September 4, 2015).
- Marketing Firm of ISRO – Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL).
- Established – 1992.
- Mini Ratna company.
- Commercial Arm of ISRO – NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
- Established – March 2019.
- Central Public Sector Enterprise.
History
You might be surprised to hear that ISRO was not the first space research center set up by the Government of India.
It had a predecessor named "INCOSPAR" (Indian National Committee for Space Research) which was set up in 1962 under the aegis of then Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru, Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, and Dr. Ramanathan under the Department of Atomic Energy.
Long before that in 1947, with the establishment of the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) Ahmedabad, known as the "Cradle of Space Research in India," Dr. Vikram Sarabhai had amassed talented and dedicated scientists, anthropologists, communicators, and social scientists from around the country to drive the Indian space mission
Later INCOSPAR was renamed ISRO on August 15, 1969, and the Government of India formed the Department of Space (DOS) in June 1972, bringing ISRO under DOS in September 1972.
VSSC (Vikram Sarabhai Space Center)
It was under INCOSPAR, the first rocket launching center of India, which was established in 1962 at the southern tip of India.
- Established in – 1962.
- Location – Thiruvananthapuram.
- First Satellite launching center of India.
- India's only rocket launching station situated near the Equator.
- Former name – Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS).
- Mecca of Rocket Science in India – St. Mary's Magdalene Church (now Space Museum).
- First Satellite Launched from TERLS – Nike Apache.
- Launched on – 1963 November 21.
- With the help of NASA (USA).
- First indigenously built rocket launched from TERLS – Rohini (RH 75)
- Launched in – 1967.
- Weight – 32 kg.
- Renamed as VSSC in – 1972.
- Submitted to UNO on - 1968 February 2.
- By Indira Gandhi.
Sriharikota
Sriharikota is a barrier island situated in the Bay of Bengal near Nellore, Andhra Pradesh.
- Established in – 1971.
- Second Satellite launching station in India.
- Epithet – Spaceport of India, Cape Kennedy of India.
- Former name – Sriharikota Range.
- Renamed as – Satish Dhawan Space Center (2002).
- Lake near Satish Dhawan Space Center – Pulicat Lake.
Rockets & Launch Vehicles
Launch vehicles or launchers or carrier rockets are rocket-propelled vehicles designed to transport a spacecraft or a satellite from the Earth's surface to outer space.
Did you know the first man to use rockets in India was Tipu Sultan?
The launchers are mainly classified into 3. They are:
- First Generation Launchers.
- Operational Launchers.
- Next Generation Launchers
First Generation Launchers
They are mainly divided into 2 categories. They are:
- Sounding Rockets – One or two-stage propellant rockets, eg: Nike Apache, Rohini; mainly for research and meteorological purposes.
- Operational Sounding Rockets – SLV & ASLV come under this category.
1. SLV (Satellite Launch Vehicle)
- Stages – 4.
- Height – 22.7 m
- Weight – 17 Ton.
- Payload capability – 40 Kg.
- First indigenously built launching vehicle – SLV-3
- First experimental flight of SLV-3 - 1979 August 10.
- Status – Partially successful.
- First successful flight of SLV-3 - 1980 July 18.
- First Indian satellite to be successfully placed in orbit by SLV-3 – Rohini (RS -1).
- Launched on – 1980 July 18.
- Under the aegis of Dr. A.P. J. Abdul Kalam.
- First Indian satellite to be launched successfully on an indigenously built launcher – Rohini.
- With this, India became the world's sixth country capable of orbital launches.
2. ASLV (Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle)
- Stages – 5.
- Height – 23.5 m
- Weight – 40 Ton.
- Payload capability – 150 Kg.
- First Launch – 1987 March 24.
- First Successful Launch – ASLV-D3.
- 1992 May 20.
- With SROSS-C weighing 106 kg.
Operational Launchers
1. PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle)
- First Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
- Epithets – The Workhorse of ISRO, The Forex earner.
- Stages – 5.
- Height – 44 m
- Weight – 40 Ton.
- Payload capability – 1500 Kg.
- Reach – 600-900 km.
- 4 part system: first & third stage uses solid fuel, second & fourth stages uses liquid fuel. Strap-on motors are also used with PSLV to augment the thrust.
- Multiple Satellite Launch Capability.
- 3 variants are deployed
- PSLV – CA (Core Alone)
- PSLV QL
- PSLV XL (Chandrayaan I & Mangalyaan)
- PSLV C21 – 100th space mission of ISRO.
- Launched on – 2012 September 9.
- 21st successful PSLV flights in a row.
- PSLV C50 is another variant that uses PSLV QL with 4 strap on boosters and will be used to launch RISAT & 9 small foreign satellites from Japan, Italy, Israel & US
- So far, PSLV has launched 50 Indian Satellites & 222 Foreign satellites for 20 countries worldwide.
2. GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle)
- Stages – 3.
- Height – 49.13 m
- Weight – 414.75 tonnes
- Payload capability - 2500 Kg.
- Reach – 36,000 km.
- First Launch - 2001, April 18.
- Used for 14 launches (2001-2008).
- First cryogenic fuel in India deployed.
- Variants – GSLV Mk. I & GSLV Mk. II.
Even if the name GSLV & GSLV MkIII sound the same, they are entirely different launchers deployed by ISRO.
Next Generation Launchers
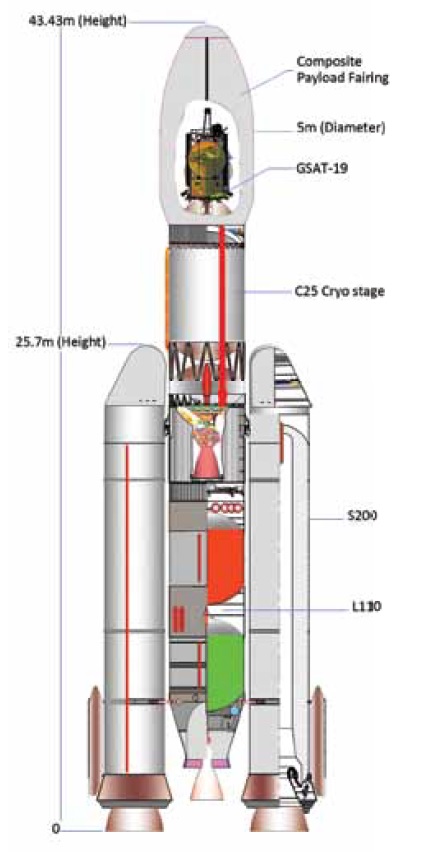
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV MkIII)
- Heaviest Rocket of India.
- Also known as LVM3.
- Stages – 3.
- Height – 43.43 m
- Weight – 640 tonnes
- Payload capability – 4000Kg.
- First Launch – 2014 December 18.
- Designed to carry 4 ton class of satellites into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) or about 10 tons to Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Successfully Launched –
- GSAT-19 (GSLV-Mk III-D1)
- GSAT-29 (GSLV MkIII-D2)
- Chandrayaan-2 (GSLV MkIII-M1).
Satellites
As a result, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) erected the first Experimental Satellite Communication Earth Station (ESCES) in Ahmedabad in 1967, which was also used to train Indian scientists and engineers.
During 1975-76, ISRO embarked on the Satellite Instructional Television Experiment (SITE), dubbed "the world's greatest social experiment."
So far India has sent 112 native satellites and 340 foreign satellites to outer space for the purpose of communication, navigation, remote sensing, meteorological studies as well as research and development studies.
Out of 112 Satellites,12 are student satellites.
- First Indian satellite – Aryabhata
- Launched on – 1975, April 19.
- Launcher – InterCOSMOS.
- With the help of the Soviet Union.
- Second Indian Satellite – Bhaskara Sega-I.
- Launched on – 1979 June 7.
- With the help of the Soviet Union.
- First Indian (indigenous) experimental Communication Satellite – APPLE (Ariane Passenger Payload Experiment).
- Launched on – 1981 June 19.
- First Meteorological Satellite launched by ISRO – Kalpana 1
- Former Name – METSAT.
- Launched on – 2002 September 12.
- Launched from – Sriharikotta.
- Launch Vehicle – PSLV C4.
- Renamed as Kalpana 1 in – A.B. Vajpayee (2003 February 5).
- First Indian Remote Sensing Satellite – CARTOSAT–1.
- Launched on – 2005 May 5.
- Launched from – Sriharikotta.
- Launch Vehicle – PSLV- C6.
- Uses – For preparing maps.
- First Satellite built by an Indian University – ANUSAT (Anna University)
- Launched on – 2009 April 20.
Launched from – Sriharikotta.
Launch Vehicle – PSLV-C12.
- First Nano Satellite – Jugnu.
- Launched on – 2011 October 12.
- Launched from – Sriharikotta.
- Launch Vehicle – PSLV-CA C18.
- Launched by – IIT Kanpur.
- Under the guidance of – Dr. N. S. Vyas.
- Uses – For providing data for disaster management and agriculture.
- First Indigenously built Radar Imaging Satellite – RISAT 1
- Launched on – 2012 April 26.
- Launched from – Sriharikotta.
- Launch Vehicle – PSLV C19.
- First dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory of India – ASTROSAT.
- Indigenously built Heaviest Satellite of India – GSAT 11 (5854 Kg).
- Launched on – 2018 December 5.
- Launched from – Kourou, French Guiana.
- Heaviest satellite launched from India – GSAT 29
- Launched on – 2018 November 14.
- Launched from – Sriharikotta.
- Smallest and Lightest Satellite in the World – KalamSAT (2019).
- Weight – 64gms.
- Designed by – Rifath Sharook;
- Took part in the global competition "Cubes in Space," for children aged 11 – 18, and his design was selected by NASA.
- Sponserd by – SpaceKidz (Chennai).
- Launched by – NASA.
- Second Satellite Launch Port (Planned) – Thoothukudi (Tamil Nadu).
Space Missions
Chandrayaan I (2008)
- First Lunar Mission of India.
- 4th nation in the world to send a lunar mission.
- ISRO Chairman – G. Madhavan Nair.
- Project Director – M. Annadurai.
- With the help of Russia.
- Weight – 1380 Kg.
- Total Cost – ₹ 386 cr.
- Launched on – 2008 October 22.
- Launched from – Sriharikotta.
- Launch Vehicle – PSLV C11.
- Designed and developed by - VSSC (TVM)
- moon impacter
- Stopped functioning in - 2009 August 29.
- Detected traces of water vapor on the surface of the moon.
- Evidence of caves formed by an ancient lunar lava flow.
Chandrayaan II (2019)
- Second Lunar Mission of India.
- ISRO Chairman – K. Sivan.
- Project Director – Muthayya Vanitha.
- Mission Director – Ritu Karidhal.
- First interplanetary mission in India to have females as both the Project Director & Mission Director.
- Weight – 3,877 kg.
- Total Cost – ₹ 978 cr.
- Launched on – 2019 July 22.
- Launched from – Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota
- Lander – Vikram.
- Rover – Pragyan.
- Launch Vehicle – GSLV Mk III-M1.
Mangalyaan
- First Asian nation to reach Mars – India.
- India became the First Country in the world to successfully reach Mars on its first attempt.
- First interplanetary Mission of India.
- MOM (Mars Orbiter Mission).
- Launched on – 2013 November 5.
- Launched from – Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota
- Launch Vehicle – PSLV-C25.
- In association with Fiji.
- Reached Mars Orbit on – 2014 September 24.
Future Programs & Missions
Gaganyaan
- ISRO Mission to get a man into space by 2022.
- With the help of Russia & France.
- No. of people being sent to space - 3. (4 are undergoing training).
- Launch Vehicle – GSLV Mk III-M1.
- Estimated Cost – ₹ 10,000 cr.
- Project Director – R. Hutton.
- Malayali scientist associated with Gaganyaan – V.R. Lalithambika.
- Humanoid Robot developed for Gaganyaa – Vyommitra.
The other future missions of ISRO being prepared at the are Aditya LM1 & Chandrayaan-3.
IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre) is also a project of ISRO which involves private participation in ISRO missions.
List of space research centers in India
In chronological order:
- Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad (1947)*
- Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station, Thumba (Kerala) (1962)
- Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), Bengaluru (1969)
- Satish Dhawan Space Center, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh (1971)
- Space Commission, Bengaluru (1972)
- Department of Space, Bengaluru (1972)
- Indian Space Research Organization Satellite Center, Bengaluru (1972)*
- National Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderabad (1974)*
- Renamed as National Remote Sensing Center (2008 September 1)
- National Centre of Earth Sciences Studies, Thiruvananthapuram (Kerala)
- College of Satellite Communication Technology, Ahmedabad
- Radio Astronomy Centre, Udhagamandalam (Ooty)
- Antrix Corporation Limited, Bengaluru (1992).
- Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota
- Space Applications Centre, Ahmedabad
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, Thiruvananthapuram
- Indian Institute of Space Science & Technology, Valiyamala, Thiruvananthapuram (2007)
- Inaugurated by – G. Madhavan Nair.
- NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), Bengaluru (2019)
* Founder – Dr. Vikram Sarabhai.
- August 12 – National Remote Sensing Day (Birthday of Dr. Vikram Sarabhai).
- Father of Space Science in the world – Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (Russia).
- Father of the Indian Space Programme – Dr. Vikram Sarabhai.
- Missile Man of India – Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam.
- Missile Woman of India – Dr. Tesy Thomas.
- Rocket Man of India – Dr. K. Sivan.
- Rocket Woman of India – Ritu Karidhal.
- First female Project Director of an interplanetary mission in India – Muthayya Vanitha (Chandrayaan-2).


%20SHAR/mcc_shar.jpg)







Post a Comment
Post a Comment