
A computer network is a collection of interconnected devices that are capable of sharing resources and information.
These devices, which can range from computers and servers to smartphones and IoT devices, communicate with each other using wired or wireless connections.
Computer networks play a crucial role in enabling communication, resource sharing, and collaboration in various environments, including homes, businesses, and the internet.
Understanding the different types of computer networks is essential for designing, implementing, and managing efficient and reliable communication systems to meet various requirements and applications.
Table of Contents
How does Computer Network Works?
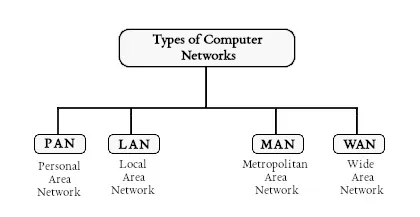
Types of Computer Networks
- PAN (Personal Area Network)
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
Personal Area Network (PAN)
PANs are networks formed by connecting devices within the personal workspace of an individual, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable devices. It
It can be wirelessly connected to the internet called WPAN and can be considered as the smallest computer network.
Bluetooth and infrared are commonly used technologies for PANs. It has a connectivity range of upto 10 m and can cover upto an area of 30ft.
Local Area Network (LAN)
LAN is a group of interconnected computers that cover a small geographical area, such as a single building or a campus and share a centralized internet connection.
They typically use media access control methods like Ethernet cables (Token-ring technology) or Wi-Fi to connect devices and are commonly found in homes, offices, and schools.
It is a widely useful network for sharing resources like files, printers, games, and other application.
LAN is comparatively inexpensive private network and the transfer of data is comparatively fast. LAN is useful for small distance communication upto 5 kms.
Current Ethernet and other IEEE 802.3 LAN technologies may carry data at speeds of up to and above 100 Gbit/s, as standardised by IEEE in 2010.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Wide Area Network (WAN)
WANs span large geographical distances, connecting devices across cities, countries, or even continents.
The internet is the largest example of a WAN.
WANs utilize technologies like leased lines, fiber optics, and satellite links to facilitate long-distance communication.
The network layer, data link layer, and physical layer are the three levels of the OSI model at which WAN technologies typically operate.
Summary of PAN, LAN, MAN & WAN
| Parameter | PAN | LAN | MAN | WAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area covered | Small area (Up to 10 m radius) | A few meters to a few Kilometers (Up to 10 Km radius) | A city and its vicinity (Up to 100 Km radius) | Entire country, continent, or globe |
| Transmission | High speed | High speed | Moderate speed | Low speed |
| Networking cost | Negligible | Inexpensive | Moderately Expensive | Expensive |
Other Computer Network Types
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
VPNs establish secure connections over a public network (usually the internet) to enable remote users to access resources and services as if they were directly connected to a private network.
VPNs are widely used for secure remote access and maintaining privacy.
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
Wireless LAN, also widely known as WLAN or WiFi (Wireless Fidelity) is based on the IEEE 802.11 standards.
WLANs utilize wireless communication technologies such as Wi-Fi to connect devices within a limited area, eliminating the need for physical cables.
They offer flexibility and mobility, making them popular in homes, businesses, and public spaces.
Campus Area Network (CAN)
AN is a type of network that interconnects multiple LANs within a limited geographic area, such as a university campus, corporate campus, or military base.
CANs are designed to provide high-speed connectivity between various buildings or locations within the campus.
Storage Area Network (SAN)
SAN is a specialized high-speed network that connects storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries, to servers.
SANs are dedicated to storage-related tasks, allowing multiple servers to access shared storage resources simultaneously. It not only makes data retrieval and storage easier, but it also saves space and enhances overall network performance.
They are commonly used in enterprise environments to centralize and manage storage resources efficiently.
Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
POLAN is a type of LAN that uses passive optical network (PON) technology to deliver high-speed connectivity over fiber optic cables.
Unlike traditional LANs that require active networking equipment like switches, POLAN utilizes passive optical splitters and combiners to distribute signals, reducing the need for powered equipment and simplifying network infrastructure.
System-Area Network (SAN)
SAN is a high-speed network architecture designed to interconnect computers and devices within a limited geographic area, typically within a single room or building.
SANs are optimized for high-performance computing and parallel processing applications, such as supercomputing clusters and data centers.
Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
EPN is a private network infrastructure owned and operated by an organization to facilitate secure communication and data exchange among its various locations, branches, and departments.
EPNs typically utilize leased lines, VPNs, or dedicated connections to ensure privacy and security of network traffic.
Home Area Network (HAN)
HAN is a type of network that connects devices within a household or residential environment.
HANs enable communication and sharing of resources among devices such as computers, smartphones, smart TVs, home automation systems, and IoT devices. Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and powerline communication are common technologies used in HANs.
Global Area Network (GAN)
📌Also Refer: Repeated Kerala PSC Questions on Computer Networks





Post a Comment
Post a Comment