A gland can be termed as an organ that produces and releases chemical substances into the bloodstream to perform a specific function in the body. The glands present in the human body can be hugely classified into two. They are
The important endocrine glands and their secreted hormones that are essential for the proper functioning of the human body are as follows:
- Endocrine glands – secretes hormones into the bloodstream.
- Exocrine glands – release their secretions such enzymes, mucus, sebum, sweat, etc. into a duct.
Important Glands in the Human body
Adrenal gland
- Also known as the 3F gland & 4S gland.
- Cap-like triangular gland located above the kidney.
- The adrenal gland is made up of 2 parts
- Outer Adrenal cortex – makes hormones called corticosteroids that help control salt-water balance in the body, the immune system, metabolism, stress response, and sexual development and function.
- There are 3 types of corticosteroids:
- Glucocorticoids – Cortisol, Cortisone,
- Mineral corticoids – Aldosterone (regulates sodium loss in the body),
- Sex hormones
- Inner Adrenal medulla – makes epinephrine/adrenaline & Noradrenaline which increases blood pressure and heart rate when the body is under stress.
- Diseases –
- Addison's disease – deficiency of cortisol
- Cushing's syndrome – overproduction of cortisol
- Cons syndrome – the overdose of aldosterone
- Vitiligo & Gynecomastia – due to the formation of tumors in the Adrenal gland.
Hypothalamus
- Located at the lower central part of the brain.
- Links the endocrine system and nervous system.
- Made up of 3 parts –
- Anterior region – also known as the supraoptic region regulates body heat and maintains the circadian rhythm. It consists of
- Supraoptic nuclei.
- Paraventricular nuclei.
- Middle region – also known as the tuberal region. It consists of
- Ventromedial nuclei – controls the appetite.
- Arcuate nuclei – released the growth hormone responsible for the growth and functioning of the human body.
- Posterior region – also known as the mammillary region. It consists of
- Hypothalamic nucleus – cause shivering, blockage of sweat, and regulates the body temperature.
- Mammillary nuclei – related to the memory function.
Pituitary gland
- Also known as "master gland" & "hypophysis."
- A pea-shaped gland at the base of the brain, just below the hypothalamus, close to the optic nerve.
- Control & regulates other glands in the body.
- It is divided into three lobes:
- Anterior pituitary – synthesis and secretion of hormones like ACTH, FSH / LH, HGH, TSH, Prolactin, MSH
- Intermediate pituitary – absent in adults.
- Posterior pituitary – synthesis and secretion of hormones like ADH & Oxytocin
- Diseases –
- Acromegaly
- Empty Sella Syndrome
- Hypopituitarism
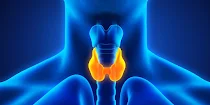
Thyroid gland
- Ductless endocrine gland.
- Butterfly shaped or bow-shaped gland located between C5 and T1 vertebrae in the neck.
- Play a vital role in the development of the brain and nervous system as well as bone development in children.
- Diseases –
- Goiter
- Hyperthyroidism – Overproduction of thyroxine hormone.
- Hypothyroidism – Underproduction of thyroxine hormone.
- Thyroid cancer –
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer
- Follicular thyroid cancer
- Medullary cancer
- Papillary thyroid cancer
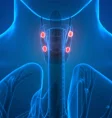
Parathyroid gland
- Four tiny glands (3-5 mm in diameter & 30-60 mg in weight) attached to the thyroid gland.
- Controls and regulates the calcium levels in the blood in the range between 9.0 & 10.1.
- Releases 2 types of hormones – Parathormone & Calcitonin.
- Diseases –
- Hyperparathyroidism – high levels of parathyroid hormone in the bloodstream.
- Hypoparathyroidism – lower levels of parathyroid hormone in the bloodstream.
Pancreas
- Gland located below the stomach and surrounded by the spleen.
- Secretes digestive enzymes such as amylase, lipase & proteases.
- Releases three hormones – Insulin, Glucagon & Somatostatin
- Diseases –
- Pancreatitis
- Pancreatic Cancer
Pineal gland
- A small pinecone-shaped gland located in the middle of the brain.
- Also known as “the third eye.”
- Regulates the body’s Circadian rhythm.
- Produces white blood cells called T-lymphocytes that fight infection and hormone, Melatonin.
- Diseases –
- Pineal Gland Tumors
- Pineal Cysts
Reproductive Glands
- Male gonads aka testes –
- Located in Scrotum.
- Secretes male hormones called Androgens (Testosterone, Androstenedione & Inhibin).
- Female gonads aka ovaries –
- Located in Pelvis.
- Secretes female hormones called Estrogen & Progesterone.
Thymus gland
- Pinkish-grey gland located deep within the chest.
- Size varies according to age, larger in children, and smaller in adults.
- Secretes hormones called Thymosin.
- Diseases –
- Myasthenia gravis – abnormal enlargement of the thymus.
- Pure red cell aplasia – occurs when there is a tumor in the thymus and the body attack its own stem cells.
- Hypogammaglobulinemia – occurs when the body is producing not enough antibodies.
All these networks of glands and their secreted hormones together constitute the Endocrine System.
Glands & their hormones: In short
| Glands | Hormones |
|---|---|
| Adrenal gland | Adrenaline, Noradrenaline, Aldosterone & Cortisol |
| Hypothalamus | Vasopressin (aka Antidiuretic hormone), GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone) |
| Pancreas | Insulin, Glucagon & Somatostatin |
| Parathyroid gland | Parathyroid hormone |
| Pineal gland | Melatonin, Serotonin (precursor to Melatonin) |
| Pituitary gland |
|
| Ovaries | Estrogen & Progesterone |
| Testes | Testosterone, Androstenedione & Inhibin |
| Thymus gland | Thymosin |
| Thyroid gland | Thyroxine (T4), Tri-iodothyronine (T3) & Calcitonin |
📝SideNotes:
- Insulin shock – Lowering blood sugar level as far as 43mg / 100ml which leads to unconsciousness and sudden death.
- also known as Severe hypoglycemia.
- Vitiligo – a condition in which the skin loses its melanocytes, the pigment cells
- Gynecomastia – Manifestation of femininity in males.













Post a Comment
Post a Comment