Kerala with its fertile soil, rain-fed rivers, backwaters, and two monsoon seasons is suitable for cultivation for both seasonal and perennial crops. Kerala is mainly an Agrarian society with rural areas solely depending on agriculture.
The implementation of the Land Reforms Act in 1963 became a stepping-stone for further reforms in Kerala's agricultural sector.
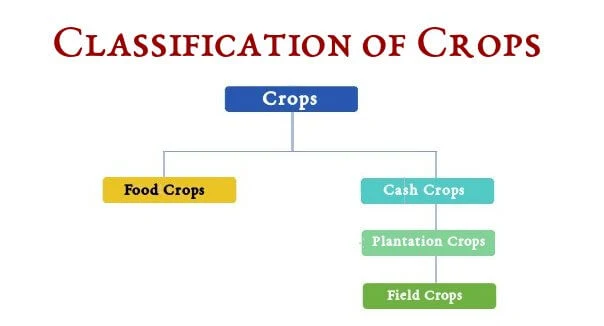
There are mainly two types of Crops. Food crops are plants grown for human consumption whereas Cash crops are plants grown to be sold for profit.
- Food Crops: Cereals & Pulses.
- Cash Crops:
- Plantation Crops: Tea, Coffee, Rubber.
- Field Crops: Cotton, Jute, Sugarcane, Oilseeds, Tobacco.
Fifteen principal crops (Rice, pulses, coconut, rubber, tea, coffee, pepper, cardamom, areca nut, ginger, nutmeg, cinnamon, tapioca, etc) are cultivated in Kerala. Plantation crops dominate the agricultural sector in Kerala.
Kharif, Rabi & Zaid Crops
Kharif Crops: Monsoon crops that are sown during the onset of the south-west monsoon season in June to September.
Rabi Crops: Winter crops that are sown from the months of October to March in the winter season.
Zaid Crops: Summer Crops that are sown between the Kharif and Rabi seasons ie, between March and June.
Main Cereal of Kerala – Rice.
Main Spices of Kerala – Cardamom, Cinnamon, Clove, Ginger, Nutmeg, Pepper, Turmeric & Vanilla.
Click here to read more about Leading Producers of Crops in Kerala
Main Crops of Kerala
1. Rice
Rice is the staple food of Kerala. More than 600 different varieties of rice are cultivated in Kerala. The rapid urbanization hugely diminished the no. of paddy fields in Kerala and a large variety of rice native to the region was lost.
Palakkad, Alappuzha, Thrissur & Kottayam accounts for 80% of the total rice production in the state and Kerala stands in 11th position in the country-wide rice production.
- Scientific Name – Oryza sativa.
- Seasons suitable for rice cultivation in Kerala – Viruppu, Mundakan & Puncha.
- Aromatic variety of rice is cultivated in – Wayanad.
- Aromatic rice variety cultivated in Wayanad – Jeerakasala & Gandhakasala.
- Saline tolerant variety of rice cultivated in Kerala – Pokkali (പൊക്കാളി).
- The place in Kerala where rice is cultivated below sea level – Kuttanad.
- 'Rice Bowl of Kerala' – Kuttanad.
- 'Rice Granary of Kerala'– Palakkad.
2. Rubber
Rubber is one of the most important cash crops in Kerala. The rubber plantations in Kerala accounts for 85% of India's total natural rubber production.
Rubber is not a native to Kerala, Dutch planters were the first to introduce rubber for cultivation in Kerala.
Kottayam district especially the regions of Meenachil and Kanjirappilly taluks is the major producer of Rubber in Kerala.
Ranni of Pathanamthitta district is another leading rubber producer in Kerala.
- Scientific Name – Hevea brasiliensis.
- Rubber Board – Kottayam.
- Land of Latex – Kottayam.
- First Rubber Park in Kerala – Airapuram.
3. Coconut
Coconut is another important crop in Kerala. India is the third-largest country in the coconut export around the world and nearly 70% of the national output of coconuts is provided by Kerala.
Coconut tree plays a pivotal role in the revenue generation of Kerala. Every part of the tree generates income, from the coir for mattresses to coconut shells for artifacts.
- Scientific Name – Cocos nucifera.
4. Spices
Ancient Kerala was famous for its spices and had trade relations with Babylonians, Egyptians, Arabs, Chinese, Greeks, and eventually Europeans dating back to 3000 B.C.E. Kerala is home to many varieties of spices and can be termed as the 'treasure house of spices.'
Kerala produces 97% of India's total black pepper output. Other important spices are cardamom, cinnamon, clove, turmeric, nutmeg, and vanilla.
- Garden of Spices/Spice Garden of India – Kerala.
- King of Spices – Black Pepper.
- Yavana Priya – Pepper.
- Scientific Name – Piper nigrum.
- Queen of Spices – Cardamom.
- Scientific Name – Elettaria cardamomum.
- Cardamom Research Station – Pampadumpara (1956).
- Largest producer of cardamom in the world – Vandanmedu (Idukki).
- Largest cardamom auction center in Kerala – Vandanmedu.
- Original Home of Cardamom – Evergreen monsoon forests of the Western Ghats.
- Princess of Spices – Vanilla.
Crop Varieties
- Black Pepper – Malabar Garbled & Tellichery Extra Bold.
- Cashew – Aanaka, Darasree, Dhanya, Mridula & Sulabha .
- Coconut – DxT & TxD (high yielding hybrid varieties).
- Tender Coconut – Chavakkad Orange Dwarf.
- Pineapple – Mauritius variety & MD2 variety.
- Rice – Annapurna, Aruna, Karuthamodan-Tall, Harsha, Jaya, Jyothy, Mangalamahsuri, etc
- Scented Rice – Chennellu, Chomala, Njavara, Kayama, Kothampalarikkayama, Kavungin-poothala, Velumbala.
- Tomato – Anagha, Mukthi & Sakthi (bacterial resistant varieties).
Govt. Schemes in Agriculture
- eNAM(e-National Agricultural Market) – online trading portal for the unified agricultural market across the country, a central govt. initiative.
- Kisan Sree – Accident insurance schemes are given by the government of Kerala to farmers.
- Kisan Abhiman – The pension scheme started by Govt. of Kerala to farmers above 60.
- Micro Irrigation Fund (MIF) – a central govt scheme with NABARD under PMKSY that provides money to the states at concessional interests to promote micro-irrigation.
- National Mission For Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) – a central govt. scheme to promote sustainable agriculture practices best suitable for region-specific ecology.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) – a national mission to improve farm productivity and conserving water resources and its management.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) – a central government-sponsored crop insurance scheme for farmers to insure their crops.
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) – a central govt. scheme under NMSA to promote traditional and organic farming through cluster farming methodology.
Read More:
📝SideNotes:
- Plant Breeding – Science of improving crop varieties.
- Agricultural Minister – P. Prasad. (as of 2025)
- Central Plantation Crops Research Institute (CPCRI) is situated in – Kasargode (1970).
- Kingdom of Pepper – India.
- First Indian State to market for Masala Bonds – Kerala.
- Kerala Infrastructure Investment Fund Board (KIIFB) – First sub-sovereign entity in India to issue Masala bond listing of ₹ 2,150 crores at the London Stock Exchange.
- Masala (Spice) Bonds – Indian rupee-denominated debt papers issued by Indian entities in overseas markets.
- First Agricultural department in Travancore was formed in – 1908.
- First Director of the Agriculture department in Travancore State – Dr. N. Kunjan Pillai.
- Father of Malayalam Farm Journalism – Dr. N. Kunjan Pillai.
- Cotton – is dispersed with the help of hairs on the seed.
- Coconut reached Kerala from – Sri Lanka.
- Red chili was brought to Kerala by the Portuguese from – Brazil.
- Cashew was brought to Kerala by – Portuguese.
- 'White Gold'*
- First introduced to prevent soil erosion.
- India is the second-largest producer and exporter of cashew in the world.
- Crop known as 'Green Gold' – Vanilla.*
- Birthplace – Mexico.
- Self Pollination not possible, so hand pollination is employed in vanilla cultivation.
- Birthplace of Papaya – Mexico.
- Rubber –
- First scientific study of rubber was done by – Charles de la Condamine.
- Synthetic rubber was first developed by – Gustave Bouchardat (1879).
- Bamboo – Poor Man's Timber.
- Green Gold.*
- Kerala accounts for approx. 7% of India's total bamboo production, of which most of these are obtained from forests of Kerala.
- Queen of the Eastern Hill Lands – Ranni.
- The creation of Nicotine in the tobacco plant starts at the – Roots.
- Transportation of food from the leaves to all parts of the plant is possible through – Phloem.
- Tamil Classic was written by Tiruttakrdeva that explores the trade relations between the ancient Roman Empire and Kerala – Jivaka Chintamani.
- _________ won the platinum award at digital Empowerment of citizens category in digital India Award 2022 – e-NAM. (Junior Manager (Quality Assurance) Civil Supplies Corporation Ltd, 2023)
* Often both Cotton as well as Cashew nut are termed as White Gold & same goes for Vanilla and Bamboo being Green Gold. Thanks Bharath for pointing that out!




1 Comments
white gold - cotton
ReplyDeletegreen gold - bamboo
Post a Comment